leetcode热题100-Java解-2025.4.6 65/100
感觉好像会回溯了
next 动态规划 贪心算法 数据结构
以及记得背八股文
207.课程表 你这个学期必须选修 numCourses 门课程,记为 0 到 numCourses - 1 。
在选修某些课程之前需要一些先修课程。 先修课程按数组 prerequisites 给出,其中 prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] ,表示如果要学习课程 ai 则 必须 先学习课程 bi 。
例如,先修课程对 [0, 1] 表示:想要学习课程 0 ,你需要先完成课程 1 。
请你判断是否可能完成所有课程的学习?如果可以,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]] 输出:true 解释:总共有 2 门课程。学习课程 1 之前,你需要完成课程 0 。这是可能的。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入:numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0],[0,1]] 输出:false 解释:总共有 2 门课程。学习课程 1 之前,你需要先完成课程 0 ;并且学习课程 0 之前,你还应先完成课程 1 。这是不可能的。
实质上是在解决一个拓扑排序问题
解法一 广度优先搜索
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 public boolean canFinish (int numCourses, int [][] prerequisites) { List<List<Integer>> edges = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { edges.add(new ArrayList <>()); } int [] indeg = new int [numCourses]; for (int [] prerequisite : prerequisites) { edges.get(prerequisite[1 ]).add(prerequisite[0 ]); indeg[prerequisite[0 ]]++; } Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { if (indeg[i] == 0 ) { queue.offer(i); } } int visited = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int u = queue.poll(); visited++; for (int v : edges.get(u)) { indeg[v]--; if (indeg[v] == 0 ) { queue.offer(v); } } } return visited == numCourses; }
解法二 深度优先搜索
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 private static final int UNVISITED = 0 ; private static final int VISITING = 1 ; private static final int VISITED = 2 ; private int [] status; private List<List<Integer>> edges; private boolean hasCycle = false ; public boolean canFinish (int numCourses, int [][] prerequisites) { status = new int [numCourses]; edges = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { edges.add(new ArrayList <>()); } for (int [] prerequisite : prerequisites) { edges.get(prerequisite[1 ]).add(prerequisite[0 ]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { if (status[i] == UNVISITED) { dfs(i); } } return !hasCycle; } private void dfs (int course) { status[course] = VISITING; for (int nextCourse : edges.get(course)) { if (status[nextCourse] == UNVISITED) { dfs(nextCourse); } else if (status[nextCourse] == VISITING) { hasCycle = true ; return ; } } status[course] = VISITED; }
208.实现 Trie(前缀树 TODO Trie 前缀树 是一种树形数据结构,用于高效地存储和检索字符串数据集中的键。这一数据结构有相当多的应用情景,例如自动补全和拼写检查。
请你实现 Trie 类:
Trie() 初始化前缀树对象。void insert(String word) 向前缀树中插入字符串 word 。boolean search(String word) 如果字符串 word 在前缀树中,返回 true(即,在检索之前已经插入);否则,返回 false 。boolean startsWith(String prefix) 如果之前已经插入的字符串 word 的前缀之一为 prefix ,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 输入 ["Trie", "insert", "search", "search", "startsWith", "insert", "search"] [[], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"]] 输出 [null, null, true, false, true, null, true] 解释 Trie trie = new Trie(); trie.insert("apple"); trie.search("apple"); // 返回 True trie.search("app"); // 返回 False trie.startsWith("app"); // 返回 True trie.insert("app"); trie.search("app"); // 返回 True
题目本身不难,但可以延伸出其他很多东西
关于 前缀树/字典树 会另写
参考 【图解算法】模板+变式——带你彻底搞懂字典树(Trie树)-CSDN博客
想明白Node[26] next和isEnd两个条件就行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 class Trie { private class TrieNode { TrieNode[] children; boolean isEnd; public TrieNode () { children = new TrieNode [26 ]; isEnd = false ; } } private TrieNode root; public Trie () { root = new TrieNode (); } public void insert (String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (char c : word.toCharArray()) { int index = c - 'a' ; if (node.children[index] == null ) { node.children[index] = new TrieNode (); } node = node.children[index]; } node.isEnd = true ; } public boolean search (String word) { TrieNode node = searchPrefix(word); return node != null && node.isEnd; } public boolean startsWith (String prefix) { return searchPrefix(prefix) != null ; } private TrieNode searchPrefix (String prefix) { TrieNode node = root; for (char c : prefix.toCharArray()) { int index = c - 'a' ; if (node.children[index] == null ) { return null ; } node = node.children[index]; } return node; } }
17. 电话号码的字母组合 给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按 任意顺序 返回。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:digits = "23" 输出:["ad","ae","af","bd","be","bf","cd","ce","cf"]
示例 2:
示例 3:
1 2 输入:digits = "2" 输出:["a","b","c"]
回溯经典题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) { if (digits == null || digits.isEmpty()) { return new ArrayList <>(); } Map<Character, String> phoneMap = new HashMap <Character, String>() {{ put('2' , "abc" ); put('3' , "def" ); put('4' , "ghi" ); put('5' , "jkl" ); put('6' , "mno" ); put('7' , "pqrs" ); put('8' , "tuv" ); put('9' , "wxyz" ); }}; List<String> combinations = new ArrayList <>(); return combinations; } public void backtrack () { }
具体题解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) { if (digits == null || digits.isEmpty()) { return new ArrayList <>(); } Map<Character, String> phoneMap = new HashMap <Character, String>() {{ put('2' , "abc" ); put('3' , "def" ); put('4' , "ghi" ); put('5' , "jkl" ); put('6' , "mno" ); put('7' , "pqrs" ); put('8' , "tuv" ); put('9' , "wxyz" ); }}; List<String> combinations = new ArrayList <>(); backtrack(phoneMap, combinations, digits, 0 , new StringBuilder ()); return combinations; } public void backtrack (Map<Character, String> phoneMap, List<String> combinations, String digits, int index, StringBuilder combination) { if ( index == digits.length()){ combinations.add(combination.toString()); return ; }else { char digit = digits.charAt(index); String letters = phoneMap.get(digit); int lettersCount = letters.length(); for (int i = 0 ; i < lettersCount; i++){ combination.append(letters.charAt(i)); backtrack(phoneMap, combinations, digits, index + 1 , combination); combination.deleteCharAt(index); } } }
39. 组合总和 给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7 输出:[[2,2,3],[7]] 解释: 2 和 3 可以形成一组候选,2 + 2 + 3 = 7 。注意 2 可以使用多次。 7 也是一个候选, 7 = 7 。 仅有这两种组合。
示例 2:
1 2 输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8 输出: [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]
示例 3:
1 2 输入: candidates = [2], target = 1 输出: []
解法一 官方题解方式
在回溯过程中,选择/跳过当前索引值等于是一个二叉树的两支
回溯可以保证能遍历到所有可能结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) { List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <>(); List<Integer> combine = new ArrayList <>(); backtrack(candidates, ans, combine, 0 , target); return ans; } public void backtrack (int [] candidates, List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> combine, int idx, int target) { if (idx == candidates.length) { return ; } if (target == 0 ) { ans.add(new ArrayList <Integer>(combine)); return ; } backtrack(candidates, ans, combine, idx + 1 , target); if (target - candidates[idx] >= 0 ) { combine.add(candidates[idx]); backtrack(candidates, ans, combine, idx, target - candidates[idx]); combine.remove(combine.size() - 1 ); } }
解法二 剪枝优化
上手先排序,难度少一半
候选数组确定为升序后
若当前数字大于目标值,则可以直接跳过后续值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) { List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <>(); List<Integer> combine = new ArrayList <>(); Arrays.sort(candidates); backtrack(candidates, ans, combine, 0 , target); return ans; } public void backtrack (int [] candidates, List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> combine, int idx, int target) { if (target == 0 ) { ans.add(new ArrayList <>(combine)); return ; } for (int i = idx; i < candidates.length; i++) { if (candidates[i] > target) { break ; } combine.add(candidates[i]); backtrack(candidates, ans, combine, i, target - candidates[i]); combine.remove(combine.size() - 1 ); } }
22. 括号生成 数字 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你设计一个函数,用于能够生成所有可能的并且 有效的 括号组合。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:n = 3 输出:["((()))","(()())","(())()","()(())","()()()"]
示例 2:
相对前面 水题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public List<String> generateParenthesis (int n) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); List<String> result = new ArrayList <>(); backtrack(stack, result, n, 0 , 0 ); return result; } public void backtrack (Stack<Integer> stack, List<String> result, int n, int left, int right) { if (left == n && right == n) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (int i : stack) { if (i == 1 ) { sb.append("(" ); }else { sb.append(")" ); } } result.add(sb.toString()); } if (left < n) { stack.push(1 ); backtrack(stack, result, n, left + 1 , right); stack.pop(); } if (right < left) { stack.push(2 ); backtrack(stack, result, n, left, right + 1 ); stack.pop(); } }
79.单词搜索 TODO 给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 。如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:
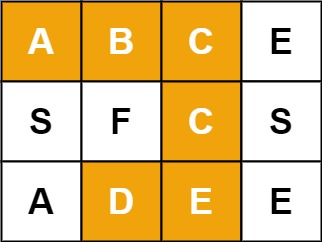
1 2 输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED" 输出:true
示例 2:
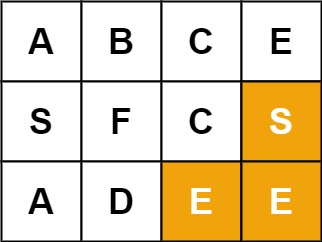
1 2 输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE" 输出:true
示例 3:
1 2 输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB" 输出:false
解一 官方题解 标准回溯
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { int h = board.length, w = board[0 ].length; boolean [][] visited = new boolean [h][w]; for (int i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { visited[i][j] = false ; } } int [][] directions = {{0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 }}; for (int i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { boolean flag = backtrack(board, visited, i, j, word, 0 , directions); if (flag) { return true ; } } } return false ; } public boolean backtrack (char [][] board, boolean [][] visited, int i, int j, String word, int index, int [][] directions) { if (board[i][j] != word.charAt(index)) { return false ; }else if (index == word.length() - 1 ) { return true ; } visited[i][j] = true ; boolean result = false ; for (int [] dir : directions) { int newi = i + dir[0 ], newj = j + dir[1 ]; if (newi >= 0 && newi < board.length && newj >= 0 && newj < board[0 ].length) { if (!visited[newi][newj]) { boolean flag = backtrack(board, visited, newi, newj, word, index + 1 , directions); if (flag) { result = true ; break ; } } } } visited[i][j] = false ; return result; }
解二 受评论区指导,开始考虑动态规划
但是思路过于依赖AI
在建立dp时使用了递归来建立,极大加大了性能开销
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { int h = board.length, w = board[0 ].length; int n = word.length(); boolean [][][] dp = new boolean [h][w][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { Arrays.fill(dp[i][j], false ); } } for (int i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { if (board[i][j] == word.charAt(0 )) { dp[i][j][0 ] = true ; } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { if (dp[i][j][0 ]) { dfs(board, word, i, j, 0 , dp); } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { if (dp[i][j][n - 1 ]) { return true ; } } } return false ; } public boolean dfs (char [][] board, String word, int i, int j, int k, boolean [][][] dp) { if (board[i][j] != word.charAt(k)) { return false ; } if (k == word.length() - 1 ) { return true ; } char ch = board[i][j]; board[i][j] = ' ' ; int [][] directions = {{0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 }}; for (int [] dir : directions) { int newi = i + dir[0 ], newj = j + dir[1 ]; if (newi >= 0 && newi < board.length && newj >= 0 && newj < board[0 ].length) { if (board[newi][newj] == word.charAt(k + 1 )) { dp[newi][newj][k + 1 ] = dp[i][j][k]; boolean result = dfs(board, word, newi, newj, k + 1 , dp); if (result) { return true ; } } } } board[i][j] = ch; return false ; }
解三 提交后发现性能开销大,对比评论区原解,发现递归时机不对
递归建立dp:
建立时需要遍历全排列
验证时只需找是否存在dp[m]\[n][k] k==n-1
但建立时开销太大了,造成整体性能开销巨大
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { int h = board.length, w = board[0 ].length; int n = word.length(); boolean [][][] dp = new boolean [h][w][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { Arrays.fill(dp[i][j], false ); } } for (int i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { if (board[i][j] == word.charAt(0 )) { dp[i][j][0 ] = true ; } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { if (dp[i][j][0 ]) { dfs(board, word, i, j, 0 , dp); } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { if (dp[i][j][n - 1 ]) { return true ; } } } return false ; } public boolean dfs (char [][] board, String word, int i, int j, int k, boolean [][][] dp) { if (board[i][j] != word.charAt(k)) { return false ; } if (k == word.length() - 1 ) { return true ; } char ch = board[i][j]; board[i][j] = ' ' ; int [][] directions = {{0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 }}; for (int [] dir : directions) { int newi = i + dir[0 ], newj = j + dir[1 ]; if (newi >= 0 && newi < board.length && newj >= 0 && newj < board[0 ].length) { if (board[newi][newj] == word.charAt(k + 1 )) { dp[newi][newj][k + 1 ] = dp[i][j][k]; boolean result = dfs(board, word, newi, newj, k + 1 , dp); if (result) { return true ; } } } } board[i][j] = ch; return false ; }
解三 先迭代建立dp数组,再递归判断是否成立,以达成剪枝目的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { int m = board.length; int n = board[0 ].length; int k = word.length(); boolean [][][] f = new boolean [k + 1 ][m + 2 ][n + 2 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= m + 1 ; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j <= n + 1 ; j++) { f[0 ][i][j] = true ; } } int [] dx = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }; int [] dy = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1 }; for (int t = 1 ; t <= k; t++) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { if (board[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] == word.charAt(t - 1 )) { for (int v = 0 ; v < 4 ; v++) { int a = i + dx[v]; int b = j + dy[v]; f[t][i][j] |= f[t - 1 ][a][b]; } } } } } return dfs(board, word, f, m, n, k); } private boolean dfs (char [][] board, String word, boolean [][][] f, int m, int n, int k) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { if (dfsHelper(board, word, f, i, j, k)) { return true ; } } } return false ; } private boolean dfsHelper (char [][] board, String word, boolean [][][] f, int i, int j, int k) { if (!f[k][i][j] || board[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] != word.charAt(k - 1 )) { return false ; } if (k == 1 ) { return true ; } char temp = board[i - 1 ][j - 1 ]; board[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] = ' ' ; int [] dx = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }; int [] dy = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1 }; for (int v = 0 ; v < 4 ; v++) { int a = i + dx[v]; int b = j + dy[v]; if (dfsHelper(board, word, f, a, b, k - 1 )) { return true ; } } board[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] = temp; return false ; }
131. 分割回文串 给你一个字符串 s,请你将 s 分割成一些 子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:s = "aab" 输出:[["a","a","b"],["aa","b"]]
示例 2:
每个子串都是回文串 这点让解法变得很简单
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public List<List<String>> partition (String s) { List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList <>(); List<String> path = new ArrayList <>(); dfs(s, 0 , path, res); return res; } public void dfs (String s, int start, List<String> path, List<List<String>> res) { if (start == s.length()) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = start; i < s.length(); i++) { if (isPalindrome(s, start, i)) { path.add(s.substring(start, i + 1 )); dfs(s, i + 1 , path, res); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } } } public boolean isPalindrome (String s, int start, int end) { while (start < end) { if (s.charAt(start) != s.charAt(end)) { return false ; } start++; end--; } return true ; }
51. N皇后 按照国际象棋的规则,皇后可以攻击与之处在同一行或同一列或同一斜线上的棋子。
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给你一个整数 n ,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题 的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个不同的 n 皇后问题 的棋子放置方案,该方案中 'Q' 和 '.' 分别代表了皇后和空位。
示例 1:
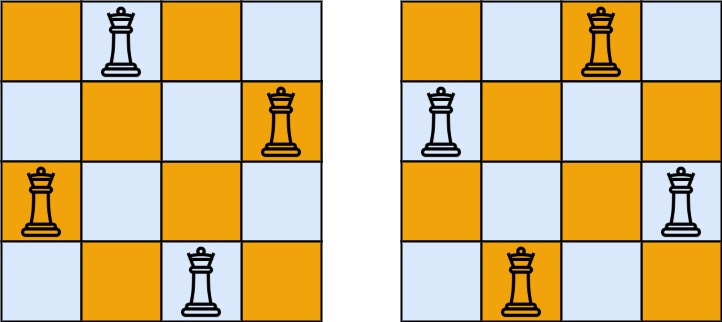
1 2 3 输入:n = 4 输出:[[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]] 解释:如上图所示,4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。
示例 2:
依然是递归回溯模板解法
注意到,在此题条件下,我们是逐行尝试皇后位置的
尝试的逻辑是:
当前行当前列尝试放置
尝试下一列
列遍历完,则尝试下一行
依此类推
所以,我们在检验放置的皇后是否合法时,只需考虑同列、左上方、右上方三个方向即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 public List<List<String>> solveNQueens (int n) { List<List<String>> solutions = new ArrayList <>(); char [][] board = new char [n][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { Arrays.fill(board[i], '.' ); } backtrack(solutions, board, 0 ); return solutions; } private void backtrack (List<List<String>> solutions, char [][] board, int row) { if (row == board.length) { solutions.add(constructSolution(board)); }else { for (int col = 0 ; col < board.length; col++) { if (isValid(board, row, col)) { board[row][col] = 'Q' ; backtrack(solutions, board, row + 1 ); board[row][col] = '.' ; } } } } private boolean isValid (char [][] board, int row, int col) { for (int i = 0 ; i < row; i++) { if (board[i][col] == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } for (int i = row - 1 , j = col - 1 ; i >= 0 && j >= 0 ; i--, j--) { if (board[i][j] == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } for (int i = row - 1 , j = col + 1 ; i >= 0 && j < board.length; i--, j++) { if (board[i][j] == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } return true ; } private List<String> constructSolution (char [][] board) { List<String> solution = new ArrayList <>(); for (char [] row : board) { solution.add(new String (row)); } return solution; }